Challenges and Goals
Diversity of primary data
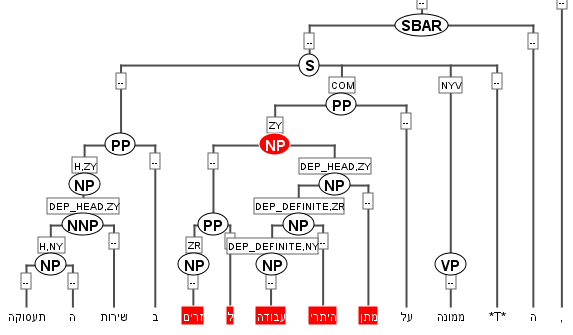
Language data can be very heterogeneous and may come from typologically diverse languages. It differs with respect to modality (written vs. spoken language, monologue vs. dialogue) and basic unit (sentence vs. discourse). In addition, special character sets (e.g. for Hindi, Old High German or the African Kwa languages) mean that full Unicode support is essential, in both visualization and search facilities. The system also offers support for right-to-left script languages, such as Arabic and Hebrew. This includes right-to-left tree layouting for treebanks in these languages.|
|
 |
|
including Regular Expressions |
|
 |
|
|
|
|
Diversity of Annotation
Data is annotated on various linguistic levels: phonetics/phonology, morpho-syntax, semantics, and information structure. The data types of the annotation range from attribute-value pairs to set relations (e.g. for annotating co-reference), directed relations/pointers (e.g. for annotating anaphoric relations), trees, and graphs (see Visualizations). Furthermore, the annotations are created with the help of different tools, i.e. different tool formats have to be supported. In order to ensure compatibility with as many formats as possible, we use the SaltNPepper converter framework, which maps a large number of formats via the metamodel Salt into relANNIS (the native format of ANNIS). 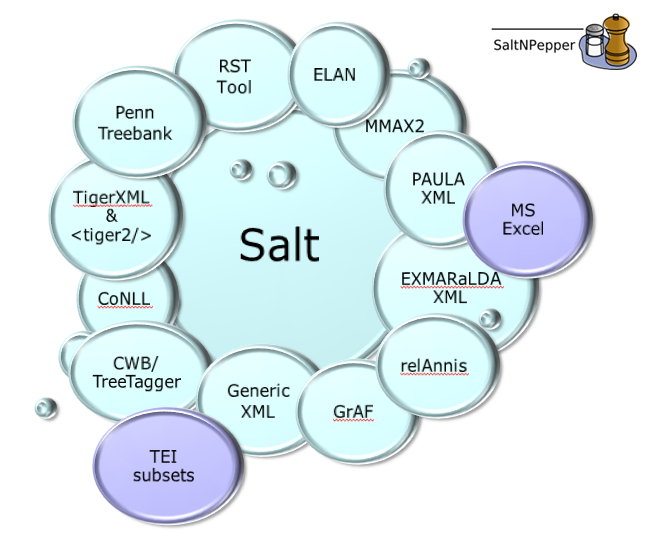
|
|
from multiple tools and formats, such as EXMARaLDA and Tiger XML, or MMAX2 and RSTTool annotations |
Multilayer Annotation
A very central requirement is support for visualizing and querying annotations on multiple layers, each layer representing one type of information, e.g. morphemic transcription, grammatical functions, pitch accents, etc. Queries must be able to simultaneously constrain all these layers and the relationships between them, making operators for the description of topological tree structures as well as span overlap necessary (see ANNIS Query Language - AQL). The system also supports parallel corpora aligned at all levels (i.e. words, sentences, syntactic phrases etc. can be aligned), and each aligned language may have its own annotation layers.
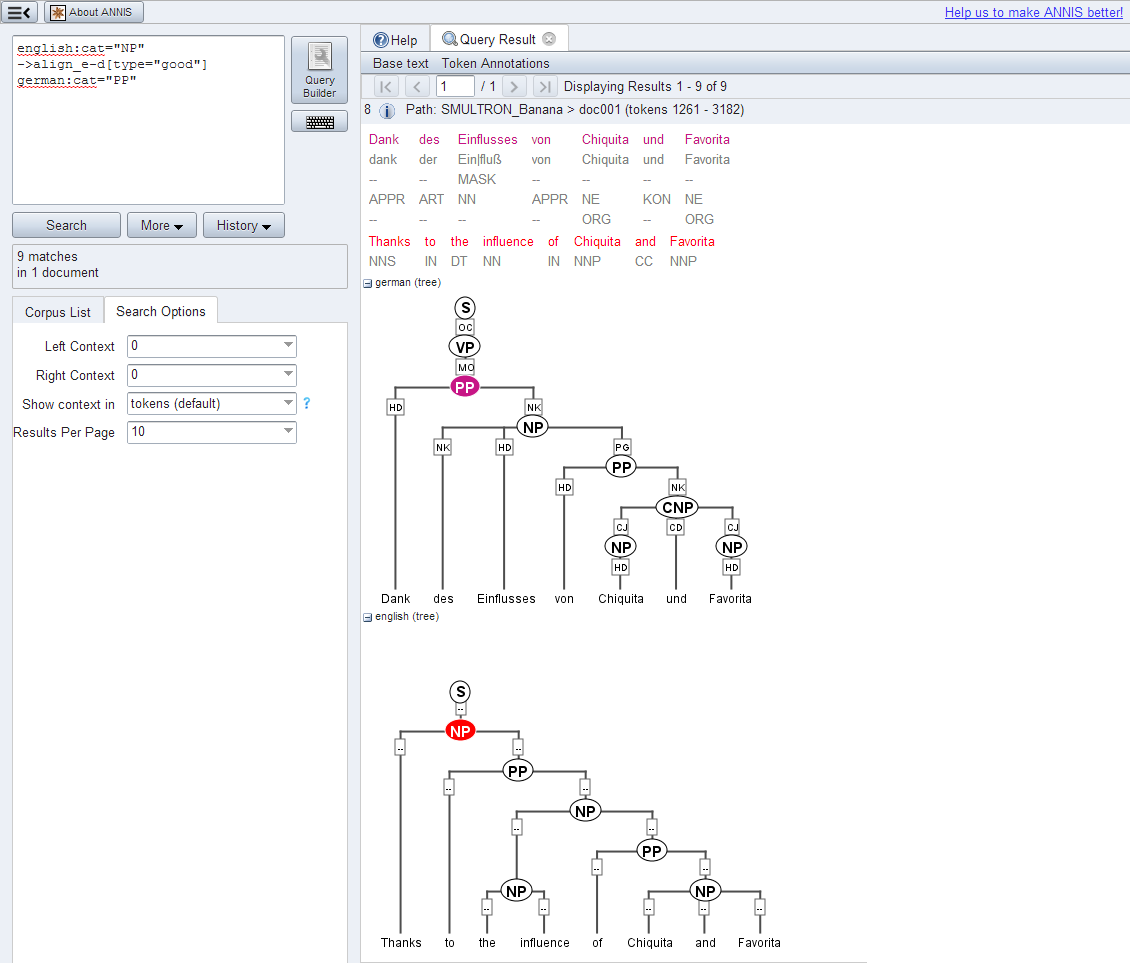 |
|
|
Accessibility
Data in the database should be easy to access and to query. Software and hardware requirements on the client side should be limited to a freely available browser (e.g. Mozilla Firefox). As little training as possible should be required, making a graphical query builder as well as corpus-specific example queries and tutorials necessary.
Performance and Scalability
Queries should return results reasonably quickly, even in large datasets. In order to realize this, the original data from XML and other formats is compiled and stored in the ANNIS backend within a relational database (PostgreSQL), which offers scalability and access speed not feasible for an XML DB, as well as native RegEx support.
